
Рисунок 1 - Виды алгоритмов и структуры алгоритмов
Алгоритм
Оценка сложности алгоритма O(n),
где О - большое, а n - количество операций
Big O - от передаваемых параметров зависит количество операций, которые будут выполнены перед тем, как алгоритм завершится.
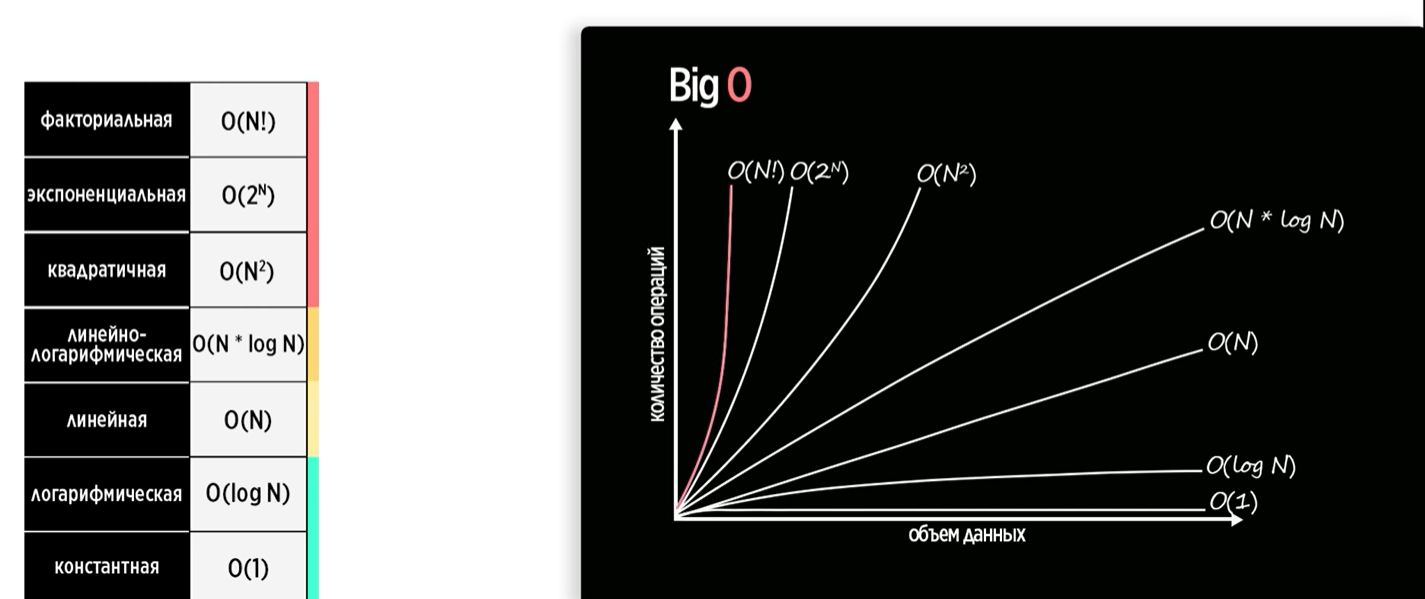
Рисунок 2 -Оценка сложности алгоритмов
Ниже будут перечислены варианты реализации Big O, от самых лёгких алгоритмов к самым тяжёлым:
- O(1) - константная зависимость: если код всегда выполняется за одно и то же время, и никак не зависит от размера входных данных.
- O(log N) - логарифмическая зависимость.
- O/_N - сублинейная сложность, где 4 = /_ 16 .
- O(N) - линейная зависимость: зависит от количества N; если алгоритм зависит более чем от одного аргумента, то указываем их все.
- O(N * log N) - линейно-логарифмическая зависимость : пример быстрой сортировки;
- O(N^2) - квадратичная зависимость: например, двойной цикл, или тройной цикл - O(N^3)
- O(2^N) - экспоненциальная зависимость: рекурсивная функция.
- O(N!) - факториальная зависимость.
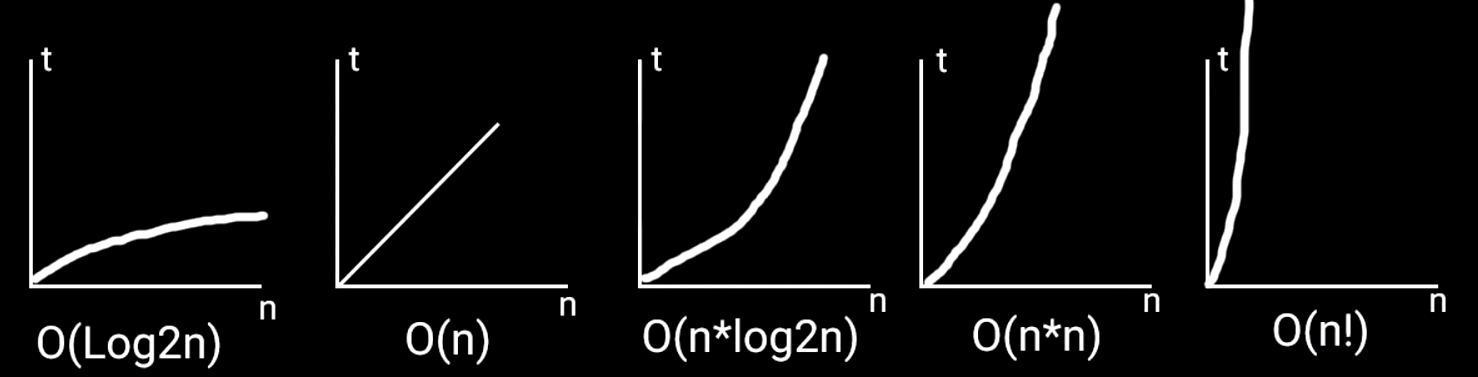
Рисунок 3 - Декомпозиция сложности алгоритмов
ВАЖНО: Алгоритм, кроме времени потребляет ещё и память компьютера.
Оцениваем сложность алгоритма
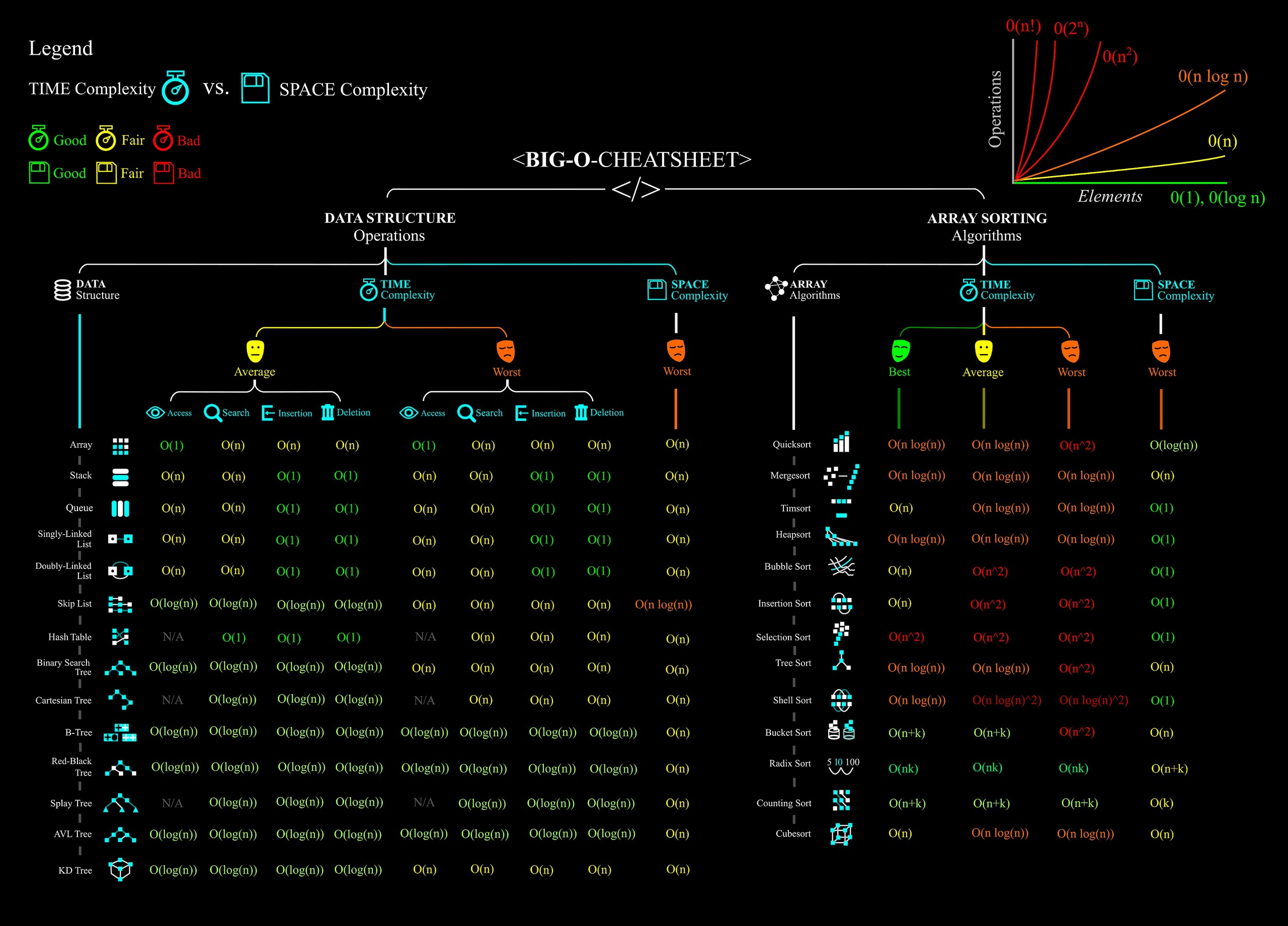
Рисунок 4 - Таблица сложности алгоритмов BIG O
Основные концепции
Линейный алгоритм O(n)
const array = [1,4,5,8,5,1,2,7,5,2,11]
let count = 0
function linearSearch(array, item) {
for (let i = 0; i < array.length; i++) {
count += 1
if (array[i] === item) {
return i;
}
}
return null
}
console.log(linearSearch(array, 1))
console.log('count = ', count)Бинарный поиск O(Log2n)
const array = [0,1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9,10,11,12,13,14,15]
let count = 0
function binarySearch(array, item) {
let start = 0
let end = array.length
let middle;
let found = false
let position = -1
while (found === false && start <= end) {
count+=1
middle = Math.floor((start + end) / 2);
if (array[middle] === item) {
found = true
position = middle
return position;
}
if (item < array[middle]) {
end = middle - 1
} else {
start = middle + 1
}
}
return position;
}
function recursiveBinarySearch(array, item, start, end) {
let middle = Math.floor((start + end) / 2);
count += 1
if (item === array[middle]) {
return middle
}
if (item < array[middle]) {
return recursiveBinarySearch(array, item, 0, middle - 1 )
} else {
return recursiveBinarySearch(array, item, middle + 1, end )
}
}
console.log(recursiveBinarySearch(array, 0, 0, array.length))
console.log(count)Сортировка O (n * n)
const arr = [0,3,2,5,6,8,1,9,4,2,1,2,9,6,4,1,7,-1, -5, 23,6,2,35,6,3,32] // [0,1,1,2,3.......]
let count = 0
function selectionSort(array) {
for (let i = 0; i < array.length; i++) {
let indexMin = i
for (let j = i+1; j < array.length; j++) {
if (array[j] < array[indexMin]) {
indexMin = j
}
count += 1
}
let tmp = array[i]
array[i] = array[indexMin]
array[indexMin] = tmp
}
return array
}
console.log(selectionSort(arr))
console.log(arr.length) // O(n*n)
console.log('count = ', count)Пузырьковая сортировка O (n * n)
const arr = [0,3,2,5,6,8,23,9,4,2,1,2,9,6,4,1,7,-1, -5, 23,6,2,35,6,3,32,9,4,2,1,2,9,6,4,1,7,-1, -5, 23,9,4,2,1,2,9,6,4,1,7,-1, -5, 23,]
let count = 0
function bubbleSort(array) {
for (let i = 0; i < array.length; i++) {
for (let j = 0; j < array.length; j++) {
if (array[j + 1] < array[j]) {
let tmp = array[j]
array[j] = array[j+1]
array[j+1] = tmp
}
count+=1
}
}
return array
}
console.log('length', arr.length)
console.log(bubbleSort(arr)) // O(n*n)
console.log('count = ', count)Быстрая сортировка O(log2n * n)
const arr = [0,3,2,5,6,8,23,9,4,2,1,2,9,6,4,1,7,-1, -5, 23,6,2,35,6,3,32,9,4,2,1,2,9,6,4,1,7,-1, -5, 23,9,4,2,1,2,9,6,4,1,7,-1, -5, 23,]
let count = 0
function quickSort(array) {
if (array.length <= 1) {
return array
}
let pivotIndex = Math.floor(array.length / 2);
let pivot = array[pivotIndex]
let less = []
let greater = []
for (let i = 0; i < array.length; i++) {
count += 1
if(i === pivotIndex)
continue
if (array[i] < pivot) {
less.push(array[i])
} else {
greater.push(array[i])
}
}
return [...quickSort(less), pivot, ...quickSort(greater)]
}
console.log(quickSort(arr))
console.log('count', count)Подробнее: Разбираемся в алгоритме быстрой сортировки с помощью JavaScript. Быстрая сортировка
Рекурсия
const factorial = (n) => {
if (n === 1) {
return 1
}
return n * factorial(n - 1)
}
// Числа фибоначчи - 1,1,2,3,5,8,13,21
const fibonachi = (n) => {
if (n === 1 || n === 2) {
return 1
}
return fibonachi(n-1) + fibonachi(n-2)
}
console.log(fibonachi(8))Graph
Graph представляет собой структуру данных с множеством вершин и соединений между графами вершин.
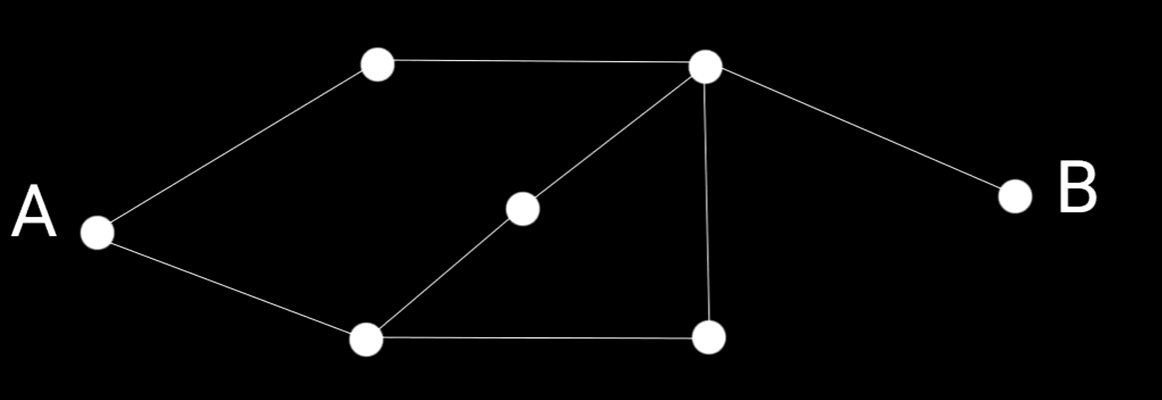
Рисунок 5 - Найти путь из точки А в точку Б с минимальным количеством шагов
Поиск в ширину
// Поиск в ширину в графе
const graph = {}
graph.a = ['b', 'c']
graph.b = ['f']
graph.c = ['d', 'e']
graph.d = ['f']
graph.e = ['f']
graph.f = ['g']
function breadthSearch(graph, start, end) {
let queue = []
queue.push(start)
while (queue.length > 0) {
const current = queue.shift()
if (!graph[current]) {
graph[current] = []
}
if (graph[current].includes(end)) {
return true
} else {
queue = [...queue, ...graph[current]]
}
}
return false
}
console.log(breadthSearch(graph, 'a', 'e'))Матрица смежности
// Матрица смежности
const matrix = [
[0,1,1,0,0,0,0],
[0,0,0,0,1,0,0],
[0,0,0,1,0,1,0],
[0,0,0,0,1,0,0],
[0,0,0,0,0,0,1],
[0,0,0,0,1,0,0],
[0,0,0,0,0,0,0],
]Поиск кратчайшего пути в графе
const graph = {}
graph.a = {b: 2, c: 1}
graph.b = {f: 7}
graph.c = {d: 5, e: 2}
graph.d = {f: 2}
graph.e = {f: 1}
graph.f = {g: 1}
graph.g = {}
function shortPath(graph, start, end) {
const costs = {}
const processed = []
let neighbors = {}
Object.keys(graph).forEach(node => {
if (node !== start) {
let value = graph[start][node]
costs[node] = value || 100000000
}
})
let node = findNodeLowestCost(costs, processed)
while (node) {
const cost = costs[node]
neighbors = graph[node]
Object.keys(neighbors).forEach(neighbor => {
let newCost = cost + neighbors[neighbor]
if (newCost < costs[neighbor]) {
costs[neighbor] = newCost
}
})
processed.push(node)
node = findNodeLowestCost(costs, processed)
}
return costs
}
function findNodeLowestCost(costs, processed) {
let lowestCost = 100000000
let lowestNode;
Object.keys(costs).forEach(node => {
let cost = costs[node]
if (cost < lowestCost && !processed.includes(node)) {
lowestCost = cost
lowestNode = node
}
})
return lowestNode
}
console.log(shortPath(graph, 'a', 'g'));Алгебраическое дерево
const tree = [
{
v: 5,
c: [
{
v:10,
c: [
{
v:11,
}
]
},
{
v:7,
c: [
{
v:5,
c: [
{
v:1
}
]
}
]
}
]
},
{
v: 5,
c: [
{
v:10
},
{
v:15
}
]
}
]
const recursive = (tree) => {
let sum = 0;
tree.forEach(node => {
sum += node.v
if(!node.c) {
return node.v
}
sum += recursive(node.c)
})
return sum
}
const iteration = (tree) => {
if (!tree.length) {
return 0
}
let sum = 0
let stack = []
tree.forEach(node => stack.push(node));
while (stack.length) {
const node = stack.pop()
sum += node.v
if (node.c) {
node.c.forEach(child => stack.push(child))
}
}
return sum
}
console.log(iteration(tree))
// console.log(recursive(tree))Кеширование
function cashFunction(fn) {
const cash = {}
return function (n) {
if (cash[n]) {
console.log('Взято из кеша', cash[n])
return cash[n]
}
let result = fn(n)
console.log('Посчитала функция = ', result)
cash[n] = result
return result;
};
}
function factorial(n) {
let result = 1
while (n != 1) {
result *= n
n -= 1
}
return result
}
const cashFactorial = cashFunction(factorial)
cashFactorial(5)
cashFactorial(4)
cashFactorial(3)
cashFactorial(4)
cashFactorial(5)
cashFactorial(1)Связанный список
class LinkedList {
constructor() {
this.size = 0
this.root = null
}
add(value) {
if (this.size === 0) {
this.root = new Node(value);
this.size += 1;
return true;
}
let node = this.root
while (node.next) {
node = node.next
}
let newNode = new Node(value)
node.next = newNode
this.size += 1
}
getSize() {
return this.size
}
print() {
let result = []
let node = this.root
while (node) {
result.push(node.value)
node = node.next
}
console.log(result);;
}
}
class Node {
constructor(value) {
this.value = value
this.next = null
}
}
const list = new LinkedList()
list.add(5)
list.add(3)
list.add(2)
list.add(5)
list.add(7)
list.print()Бинарное дерево
class BinaryTree {
constructor() {
this.root = null
}
add(value) {
if (!this.root) {
this.root = new TreeNode(value)
} else {
let node = this.root
let newNode = new TreeNode(value)
while (node) {
if (value > node.value) {
if (!node.right) {
break
}
node = node.right
} else {
if (!node.left) {
break
}
node = node.left
}
}
if (value > node.value) {
node.right = newNode
} else {
node.left = newNode
}
}
}
print(root = this.root) {
if (!root) {
return true;
}
console.log(root.value);
this.print(root.left)
this.print(root.right)
}
}
class TreeNode {
constructor(value) {
this.value = value
this.left = null
this.right = null
}
}
const tree = new BinaryTree()
tree.add(5)
tree.add(2)
tree.add(6)
tree.add(2)
tree.add(1)
tree.print()Коллекции
const map = new Map()
const objKey = {id:5}
map.set(objKey, "ulbi tv")
console.log(map.get(objKey));
const set = new Set()
set.add(5)
set.add(5)
set.add(5)
set.add(5)
set.add(5)
set.add(4)
set.add(3)
console.log(set)